SURE 4. Dünya Konferansı (The 4th SURE World Conference) 16-19 Temmuz 2025 Tarihleri Arasında İstanbul’da Yıldız Teknik Üniversitesi Ev Sahipliğinde Düzenlendi.

Istanbul Charter
For Conservation and Perception of Urban Nature
Society for Urban Ecology
Urban nature encompasses the totality of natural elements present in urban spaces, including their ecosystemic functional relationships and their use. Urban nature includes remnants of native ecosystems, patches of agricultural areas embedded within the urban fabric or around urban areas, all types and scales of designed urban green spaces, and novel wild urban ecosystems.
Importance
- Urban nature is in a critical situation worldwide. The reduction of biodiversity loss is accelerated by climate change and multiple other factors.
- Urban nature provides fundamental ecosystem services, with a powerful capacity for environmental risk reduction, playing a vital role in supporting human health.
- Enhancing residents' perception and appreciation of urban nature can increase public support for conservation initiatives, further promote sustainable urban development, and improve the quality of urban life.
Targets
- Promoting multistakeholder engagement for empowerment of urban nature issues provides a shared home for humans and nature. Enhancing stakeholders’ awareness, understanding, and sense of participation regarding the benefits of nature, actively promoting the engagement of communities for urban nature, and building better governance for a better, socio-ecologically resilient urban living environment contribute to this target.
- An effective dialogue between professionals, citizens and decision-makers, by enriching their knowledge, understanding, and responsibility regarding the benefits of nature, and formulating better institutions for a better urban living environment is necessary.
- Establishing and improving urban ecological monitoring and assessment systems to regularly track the efficacy of conservation efforts for urban nature.
- Carefully reflecting dominant societal paradigms, worldviews and plural values to recognize and prioritize human-nature interconnectedness in cities and beyond.
- Considering urban land-use teleconnection and material human-nature connections (e.g., resources, food), not strictly confined to urban boundaries, fostering social-ecological justice for human and non-human persons.
Challenges and opportunities
- Taking effective conservation measures along urbanization gradients, particularly in high-density and socially marginalized urban sectors where natural areas are limited.
- Promoting active public engagement in conservation activities and enhancing urban residents’ awareness about the importance of the natural environment, especially for more spontaneous nature and living together with urban wildlife.
- Coordinating interdisciplinary and cross-sectoral collaboration to strengthen comprehensive mechanisms for urban nature conservation and public perception.
- Preserving existing natural elements in periurban areas and integrating these features into urban nature through urban design and urban reconstruction.
- Promoting urban nature as a foundation for resilient, short food supply chains through the integration of urban agriculture and green infrastructure, with emphasis on edible plants and trees, contributing to food security, sustainability, and public engagement.
Methods
- Promoting urban nature conservation through interdisciplinary collaboration and technical support, employing spatial planning methodologies, including GIS, wildlife and animal monitoring, biodiversity-inclusive design and AI.
- Applying innovative knowledge, methods, and technologies to support the management of urban nature, respecting natural processes by reducing the load of management input (do less).
- Strengthening public participation and education by fostering communities’ co-creation and nature-based experiences and activities to raise conservation awareness of residents and nature understanding as a fundamental aspect of kids’ learning in schools.
- Developing clear and actionable indicators for urban nature conservation, integrating them into urban development strategies and spatial planning instruments at local, regional, and national levels, with the goal of increasing urban biodiversity.
- Society engagement, both formal and informal, is crucial in more inclusive approaches to space management. The participatory planning methods, smart and digital technologies, such as remote sensing and data-driven platforms, can contribute to more resident-oriented planning and management.
- Establishing urban living labs to experiment together with urban decision makers, practitioners, residents, and nature on how to overcome social-ecological-technological and structural challenges which constrain urban ecology in, of, and for cities.
Cooperation
- Promoting in-depth exchanges between fast urban developing China and traditional and long-experienced urban development in Europe in the field of urban nature conservation and perception, particularly in policy development, practical implementation, and scientific research, through international cooperation bridges between countries and learning from different experiences.
- Establishing a continuous international platform for dialogue and collaboration on urban nature conservation and perception, embracing plural values and perspectives.
- Facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration among experts from different fields of experience, such as urban planning, ecology, landscape architecture, sociology, psychology, anthropology, and related fields, to develop integrated strategies or frameworks for urban nature conservation and perception.
- Partnerships and exchange of experiences between cities are important, especially in terms of market preference trends that determine the actions of developers.
- Strengthening transdisciplinary, multi-sectoral cooperation by encouraging collaboration among researchers, practitioners, decision-makers, and non-governmental organizations to bridge policymaking, scientific research, and practical application effectively.
İstanbul Bildirgesi
Kent Ekolojisinin Korunması ve Algılanması İçin
Kentsel Ekoloji Derneği
Kent ekolojisi, kentsel alanlarda bulunan tüm doğal unsurları, bunların ekosistem işlevselliğine dayalı ilişkilerini ve kullanım biçimlerini kapsar. Kent ekolojisi; yerli ekosistem kalıntılarını, kentsel doku içinde veya çevresinde yer alan tarım alanı parçacıklarını, her ölçekteki tasarlanmış yeşil alanları ve yeni ortaya çıkan vahşi kentsel ekosistemleri içerir.
Önemi
- Küresel ölçekte kent ekolojisi kritik bir durumdadır. Biyoçeşitlilik kaybı, iklim değişikliği ve diğer birçok etken nedeniyle hızla artmaktadır.
- Kent ekolojisi, temel ekosistem hizmetleri sunar; çevresel riskleri azaltma kapasitesi yüksektir ve insan sağlığını desteklemede hayati bir rol oynar.
- Kent sakinlerinin kent ekolojisine yönelik algı ve takdirinin artırılması, koruma girişimlerine kamu desteğini güçlendirebilir; bu da sürdürülebilir kentsel gelişimi teşvik eder ve kentsel yaşam kalitesini yükseltir.
Hedefler
- Kent ekolojisi konularının güçlendirilmesi için çok paydaşlı katılımın teşvik edilmesi, insanlarla doğa için ortak bir yaşam alanı sağlar. Doğanın faydalarına dair paydaşların farkındalık, anlayış ve katılım duygularının artırılması, toplulukların kent ekolojisine yönelik etkin katılımının teşvik edilmesi ve daha iyi bir sosyo-ekolojik dayanıklılığa sahip kentsel yaşam ortamı için yönetişimin güçlendirilmesi bu hedefe katkı sağlar.
- Uzmanlar, vatandaşlar ve karar vericiler arasında etkin bir diyalog kurulması; bu aktörlerin doğanın faydalarına yönelik bilgi, anlayış ve sorumluluklarının artırılması ve daha iyi bir kentsel yaşam ortamı için daha işlevsel kurumların oluşturulması gereklidir.
- Kent ekolojisinin korunmasına yönelik çabaların etkinliğini düzenli olarak izlemek amacıyla, kentsel ekolojisini izleme ve değerlendirme sistemlerinin oluşturulması ve geliştirilmesi.
- Kentlerde ve ötesinde insan-doğa ilişkisinin önemini kabul etmek ve önceliklendirmek amacıyla, baskın toplumsal paradigmalar, dünya görüşleri ve çoğulcu değerlerin dikkatle yansıtılması.
- Yalnızca kent sınırlarıyla sınırlı olmayan, kentsel arazi kullanımının uzak etkileri (teleconnection) ile maddi insan-doğa bağlantılarının (örneğin kaynaklar, gıda) dikkate alınması; insan ve insan olmayan varlıklar için sosyal-ekolojik adaletin teşvik edilmesi.
Zorluklar ve Fırsatlar
- Kentsel yayılma boyunca, özellikle doğal alanların sınırlı olduğu, yüksek yoğunluklu ve sosyal açıdan dezavantajlı kentsel bölgelerde etkili koruma önlemlerinin alınması.
- Kendiliğinden gelişen doğa biçimleri ve kentsel yaban hayatıyla bir arada yaşamaya yönelik farkındalığı artırarak, koruma faaliyetlerine halkın aktif katılımının teşvik edilmesi.
- Kent ekolojisinin korunması ve kamu algısının güçlendirilmesi için disiplinler arası ve sektörler arası işbirliğinin koordine edilmesi.
- Kentin etrafındaki doğal unsurların korunması ve bu unsurların kentsel tasarım ve kentsel dönüşüm yoluyla kent ekolojisine entegre edilmesi.
- Kentsel tarım ve yeşil altyapı aracılığıyla yenilebilir bitkiler ve ağaçlara odaklanarak, gıda güvenliği, sürdürülebilirlik ve halkın katılımına katkı sağlayan dayanıklı, kısa gıda tedarik zincirlerinin temeli olarak kent ekolojisinin teşvik edilmesi.
Yöntemler
- Disiplinler arası iş birliği ve teknik destekle, kent ekolojisi korumanın teşvik edilmesi; bu süreçte CBS (Coğrafi Bilgi Sistemleri), yaban hayatı ve hayvan izleme, biyoçeşitliliği gözeten tasarım ve yapay zekâ gibi mekânsal planlama yöntemlerinin kullanılması.
- Kent ekolojisi yönetimini desteklemek için yenilikçi bilgi, yöntem ve teknolojilerin uygulanması; yönetim girdilerini azaltarak (daha az müdahale) doğal süreçlere saygı duyulması.
- Toplulukların ortak üretimi ve doğa temelli deneyim ve etkinlikleri destekleyerek, halkın katılımı ve eğitimin güçlendirilmesi; özellikle çocukların okulda doğayı anlamalarının ve koruma farkındalıklarının artırılması.
- Kentsel biyoçeşitliliğin artırılması amacıyla; kent ekolojisinin koruması için net ve uygulanabilir göstergelerin geliştirilmesi ve bu göstergelerin yerel, bölgesel ve ulusal düzeylerde kentsel gelişim stratejileri ve mekânsal planlama araçlarına entegre edilmesi.
- Toplumun hem resmi hem gayriresmi olarak katılımı, mekânsal yönetimde daha kapsayıcı yaklaşımlar için kritiktir. Katılımcı planlama yöntemleri, uzaktan algılama ve veri odaklı platformlar gibi akıllı ve dijital teknolojiler, daha sakin odaklı planlama ve yönetim süreçlerine katkı sunabilir.
- Kentsel karar vericiler, uygulayıcılar, kent sakinleri ve doğa ile birlikte sosyal-ekolojik-teknolojik ve yapısal engellerin nasıl aşılabileceğini birlikte deneyimlemek amacıyla kentsel yaşam laboratuvarlarının kurulması.
İş Birliği
- Kent ekolojisinin korunması ve algılanması alanında, özellikle politika geliştirme, pratik uygulama ve bilimsel araştırma boyutlarında, hızlı kentleşen Çin ile uzun bir kentsel gelişim geçmişine sahip Avrupa arasında uluslararası iş birliği köprüleri kurarak ve farklı deneyimlerden öğrenerek derinlemesine bilgi alışverişini teşvik etmek.
- Kent ekolojisinin korunması ve algılanması konusunda, çoğulcu değerleri ve bakış açılarını kapsayan sürekli bir uluslararası diyalog ve iş birliği platformunun kurulması.
- Kentsel doğa koruma ve algısına yönelik bütüncül stratejiler veya çerçeveler geliştirmek amacıyla, kentsel planlama, ekoloji, peyzaj mimarlığı, sosyoloji, psikoloji, antropoloji ve ilgili diğer alanlardan uzmanlar arasında disiplinler arası iş birliğini kolaylaştırmak.
- Özellikle geliştiricilerin eylemlerini belirleyen piyasa tercih eğilimleri bağlamında, şehirler arası deneyim ve ortaklık alışverişi önemlidir.
- Politika yapımı, bilimsel araştırma ve pratik uygulamalar arasında etkili köprüler kurmak amacıyla araştırmacılar, uygulayıcılar, karar vericiler ve sivil toplum kuruluşları arasında disiplinler ötesi ve çok sektörlü iş birliğinin güçlendirilmesi.

4th SURE World Conference in Istanbul, Turkey
Between 16 and 19 July 2025, the 4th SURE World Conference took place in Istanbul, Turkey, under the theme ““Cities Under Global Social Transformations: Embracing Change for a Greener Future”. Hosted at Yıldız Technical University, the conference brought together scholars, practitioners, and decision-makers from around the world to exchange knowledge, build networks, and inspire future actions in urban ecology.
Core topics included:
- Urban biodiversity and ecosystem services
- Nature-based solutions and climate resilience
- Green infrastructure and public health
- Community engagement and environmental and multi-species justice
- Urban planning, transformation, and governance
- Inter- and Transdisciplinary Approaches to Urban Ecology
- Green and Blue Infrastructure in Urban Design
- Water and Soil in Urban Sustainability
- Citizen Participation and Urban Governance
- Socio-Ecological Approaches and Equity
- Technological Innovations and AI in Urban Planning
- Urban Soundscapes and Cultural Perception
- Nature Education and Youth Engagement
The conference hosted a majority of participants from the People's Republic of China, Germany, Turkey, Romania, the Russian Federation, and Poland. A total of 498 individuals were listed as authors of the presented papers. An analysis of the country distribution shows that out of 134 papers in total, 23 were presented online. Authors from 54 different countries contributed to the papers either individually or in collaboration with others (Figure 1).
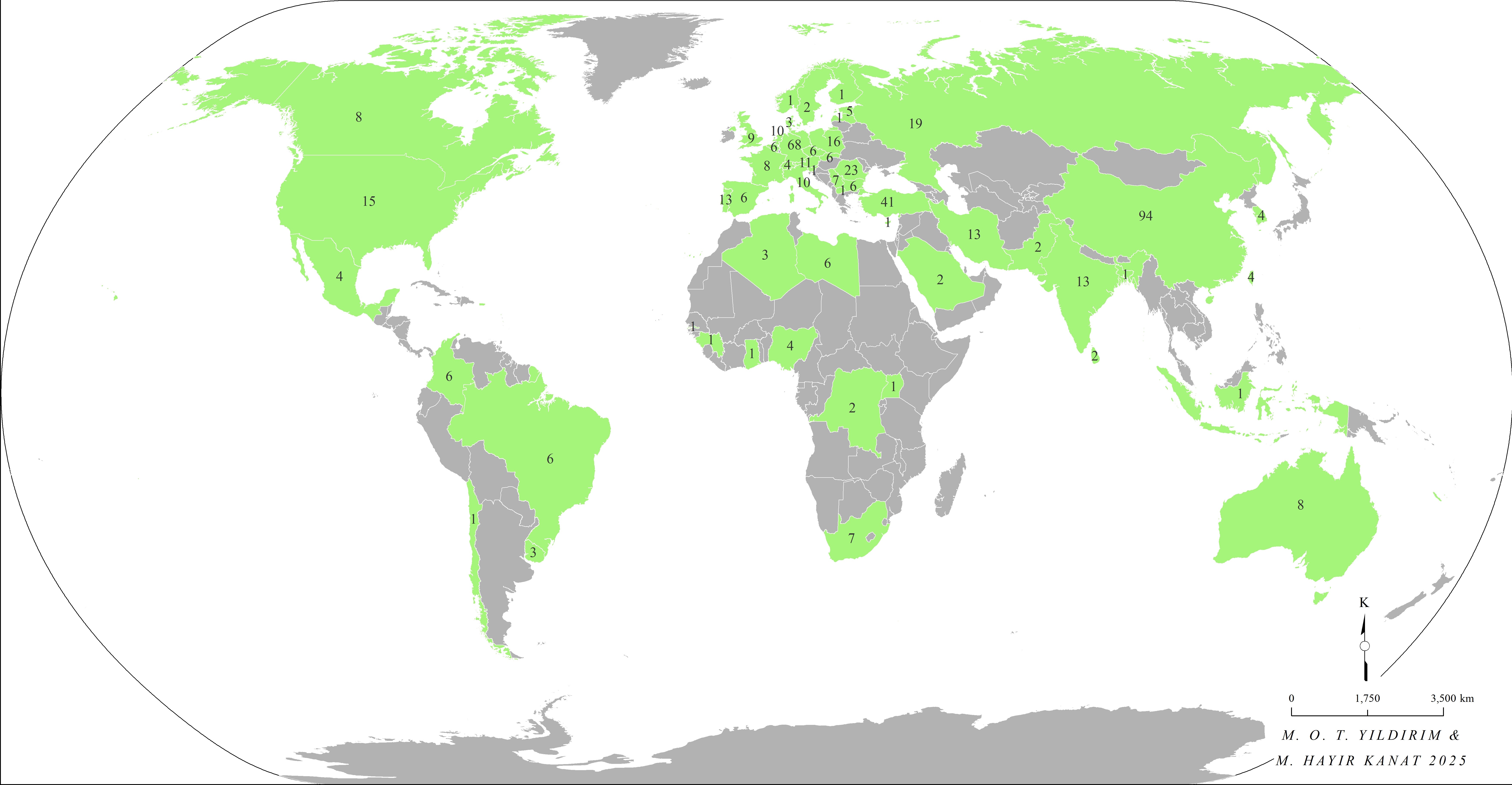
Figure 1. Geographic Distribution of the 498 Scholars Listed as Authors of Papers Presented at the Conference (from 54 Countries)
More than 200 participants from over 31 countries attended the event to explore inter- and transdisciplinary approaches to sustainable urban development, nature-based solutions, and the role of urban nature in climate adaptation and social well-being. The program featured inspiring keynote speeches, thematic sessions, interactive workshops, and field excursions across Istanbul’s diverse urban landscape. In total, the conference welcomed 133 paid participants, including 114 paper presenters and 19 listeners, representing 31 different countries (Figure 2). Thanks to the hybrid format, the event was also accessible to interested individuals who could follow the sessions as passive participants free of charge via links shared in the program.
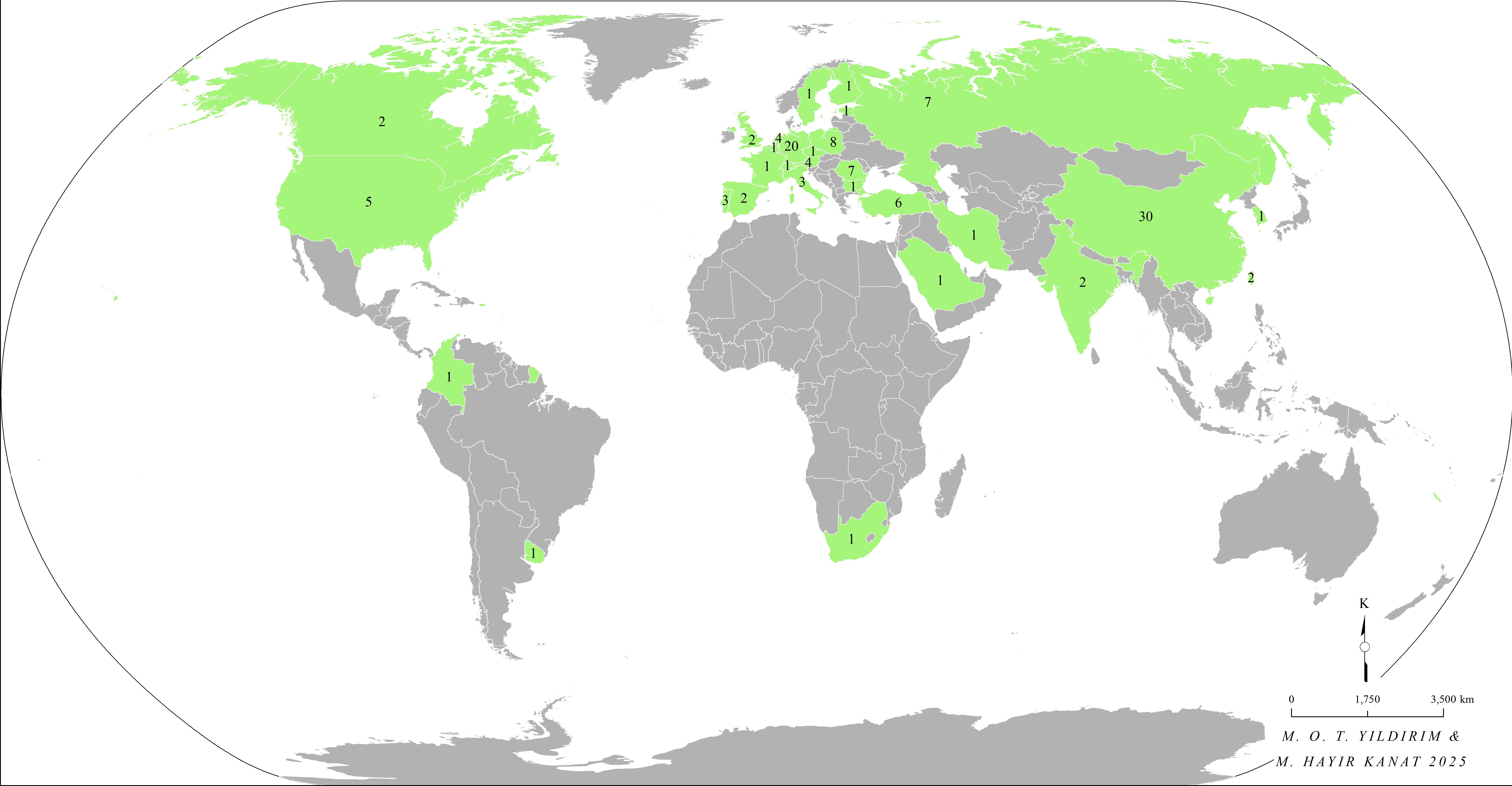
Figure 2. Country Breakdown of Registered Participants Who Delivered Presentations at the Conference (Paid Paper Presenters)
Opening Reception
On the evening of the first day, the opening reception was held with a large turnout. Scientists from various countries gathered in a friendly and dynamic setting where they exchanged ideas not only socially but also scientifically. The event provided a valuable opportunity for networking, and many participants engaged in discussions about potential future collaborations, brainstorming project ideas shaped by interdisciplinary approaches (Photo 1).
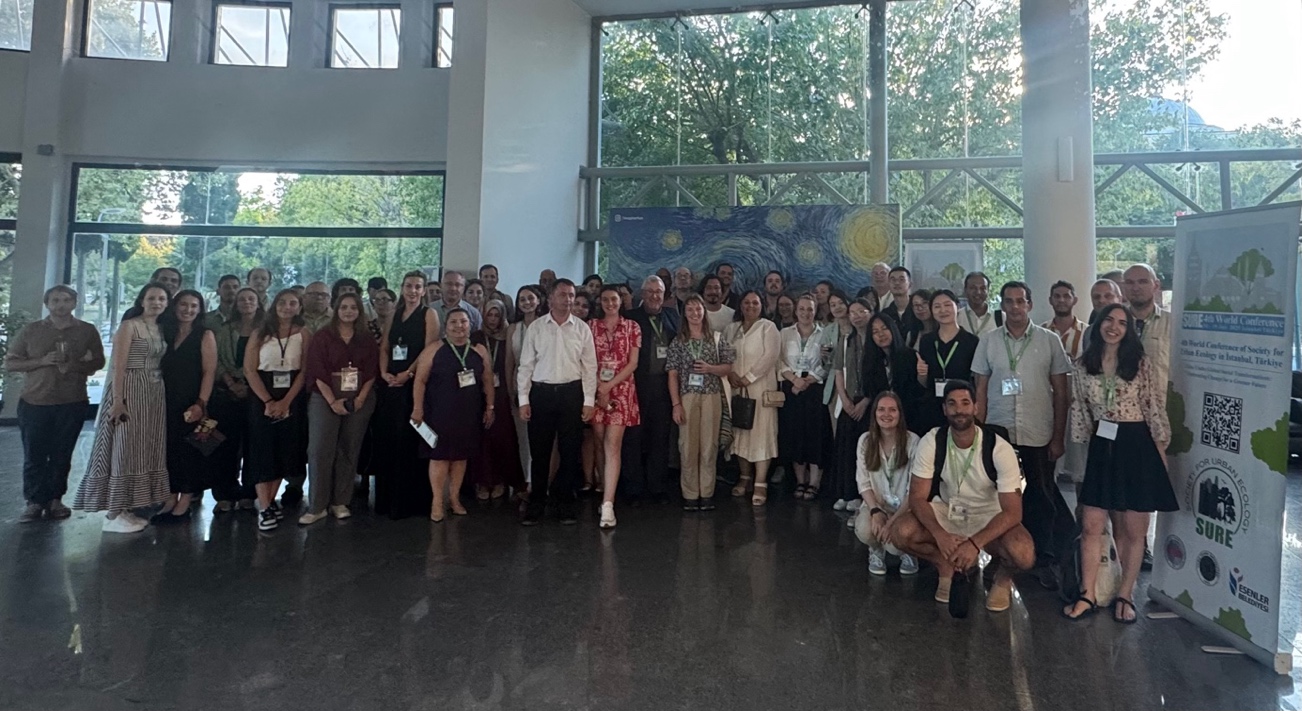

Photo 1: From the Opening Reception of the 4th SURE World Conference (ãGizem Anayol)
SURE General Assembly Meeting
At the end of the second day of the conference, the SURE General Assembly Meeting was held. During the meeting, Prof. Dr. Jürgen Breuste (President), Prof. Dr. Martina Artmann (Secretary General), and Prof. Dr. Cristian Ioja (Treasurer) presented recent activities of the association and provided an overview of the work carried out over the past four years.
It was highlighted that SURE actively encourages the participation of young people by offering free membership to students and supporting their attendance at conferences.
Regional representatives reported that SURE’s sections in China, Iran, Southeastern Europe, and Central Europe are actively involved in various initiatives. Among these, regional conferences and summer schools stand out as key activities.
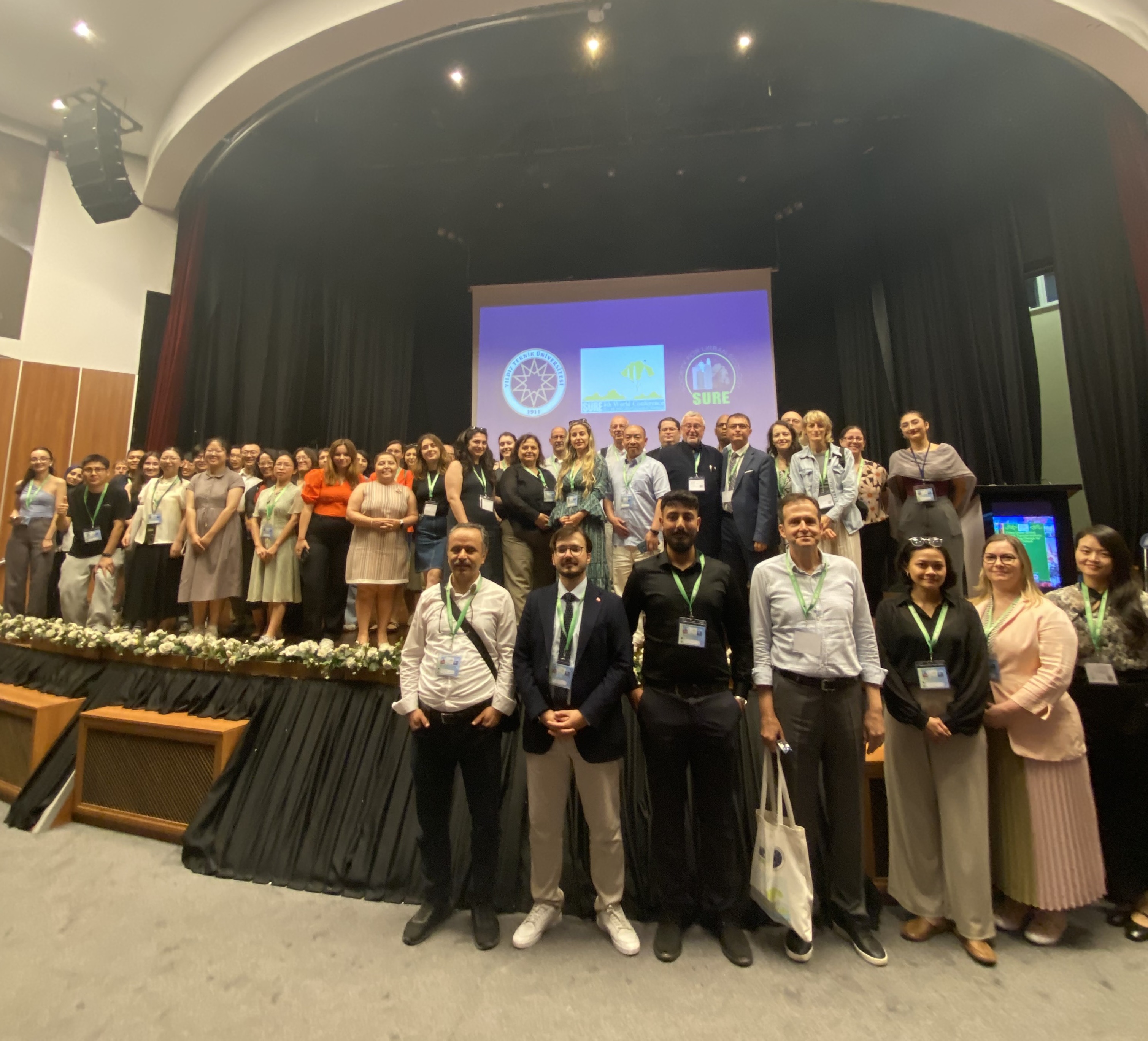

Photo 2: Participants of the SURE General Assembly (ãGizem Anayol)
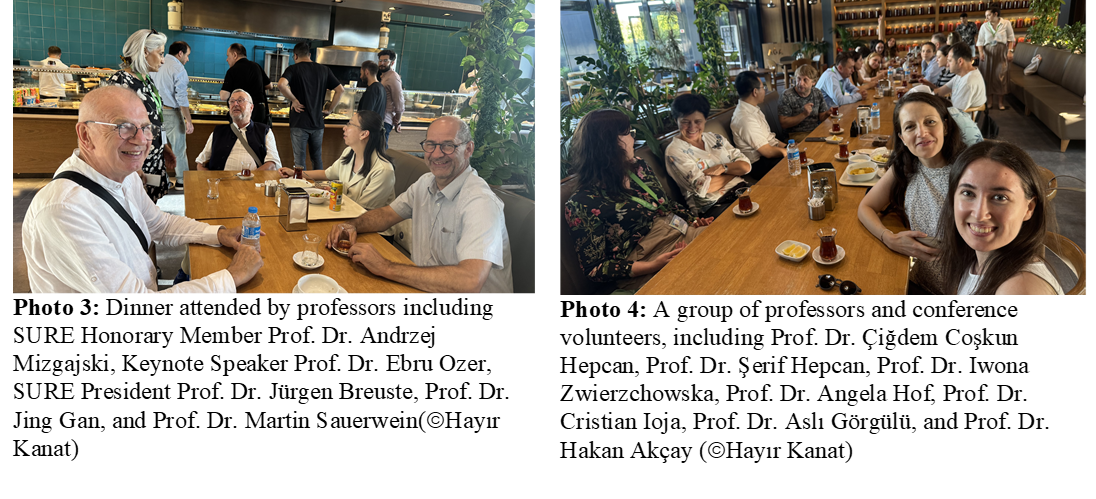
Dinner with Conference Members and Volunteers
On the third day of the conference, prominent figures of the 4th SURE World Conference and the dedicated volunteers who worked diligently to organize the event shared a dinner together at AĞA Restaurant located on the Yıldız Technical University campus (Photo 3).

Excurtion Day
On the fourth day of the conference, participants had the opportunity to experience one of the world’s most significant straits — the Bosphorus — which separates Asia and Europe. As part of the technical tour, they observed the city’s skyline and urban development along the route from Eminönü to Anadolu Kavağı.
A highlight of the conference was the SURE Sino-European Workshop and the co-creation of the Istanbul Charter for Conservation and Perception of Urban Nature, which emphasizes collaborative and inclusive strategies for protecting urban ecosystems.
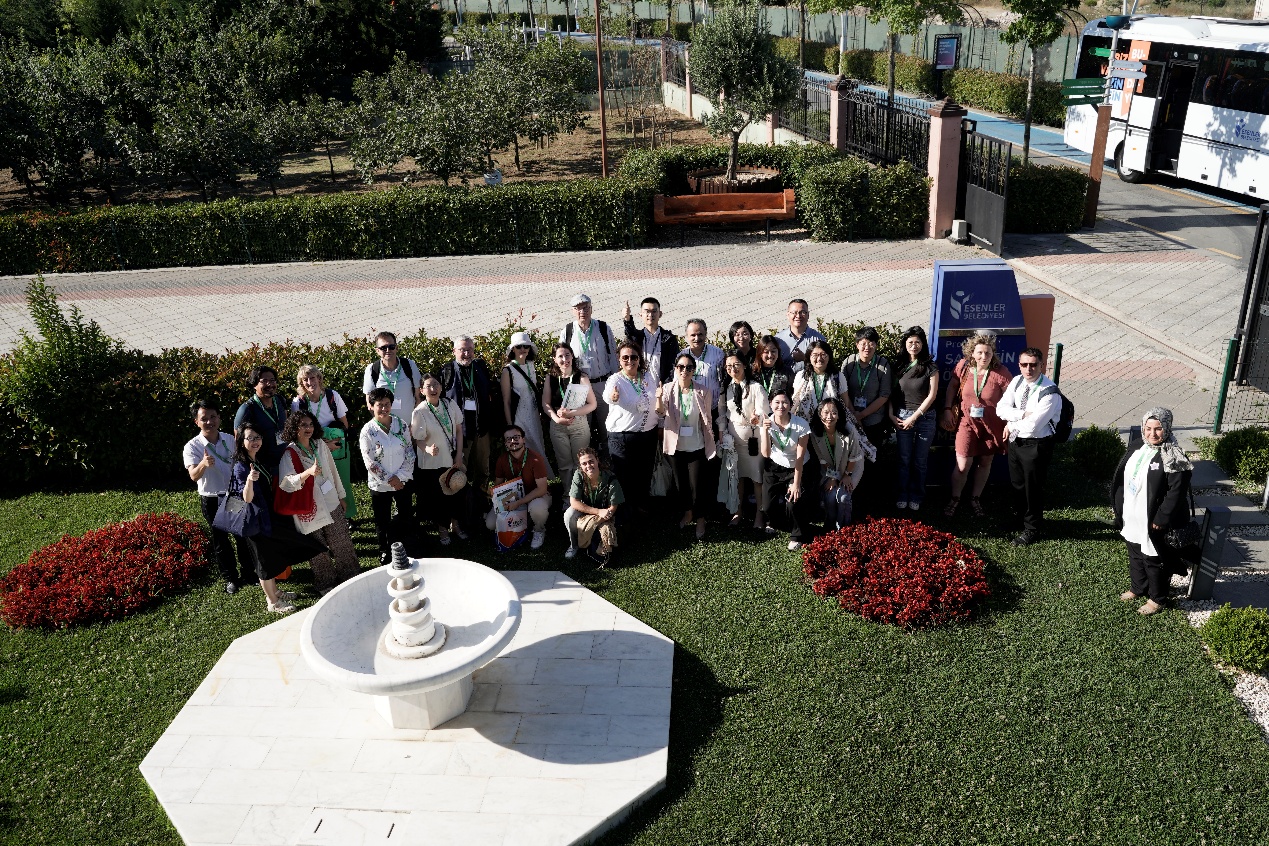

Foto: SURE Sino-European Workshop Team (ãTao Wu)
The SURE Executive Committee extends its heartfelt thanks to Prof. Dr. Meryem Hayir Kanat, Prof. Dr. Cigdem Coskun Hepcan, and all members of the Organizing Committee, including the dedicated teams from Yildiz Technical University and other supporting universities. Their commitment and hospitality throughout the conference were truly appreciated. The event once again highlighted the global significance of urban ecology in building more just, healthy, and resilient cities.
We are already looking forward to the 5th SURE World Conference in 2028 – stay tuned!